Years of extensive wildland fire suppression in the Southwest has left many forests with unnaturally high levels of forest fuels, like dense undergrowth and thick litterfall. This has changed the natural fire ecology from low, fast-burning wildfires, to much larger crown fires that kill trees and undermine landscape integrity. In 2010, a wildfire and subsequent flooding on the east side of the San Francisco Peaks, just north of Flagstaff, Arizona, caused over $150 million in combined suppression and recovery. A similar wildfire in either of the two Flagstaff watersheds could potentially flood much of downtown and/or disrupt 50 percent of the city’s water supply, resulting in significant long-term financial and life-style impacts within the community. Recognizing the need for preventative action, a partnership between the city, county, state, and federal governments, with support from local non-profit and for-profit organizations, has resulted in the Flagstaff Watershed Protection Project (FWPP). With Flagstaff Wildland Fire Management Officer Paul Summerfelt coordinating FWPP activities, FWPP plans to mitigate the risk of potentially devastating wildfires in Flagstaff’s critical watershed areas by managing forest fuels and restoring natural ecosystem functions. This will include thinning out dense forests and reintroducing a low-intensity fire regime. To fund FWPP, Flagstaff passed a $10 million municipal bond with 74 percent approval rate, making FWPP the only forest restoration work on National Forests funded through municipal bonds.

Reducing the Risks of Catastrophic Wildfires in Flagstaff
About This Project

“The strength of a management group is much better when it’s not just a single agency. When you get different people involved, they see things differently and everybody brings something into the collaborative process… If you want to go fast go by yourself, but if you want to make a difference, go with others.”— Paul Summerfelt, Flagstaff Fire Department’s Wildland Fire Management Officer
Download this case study »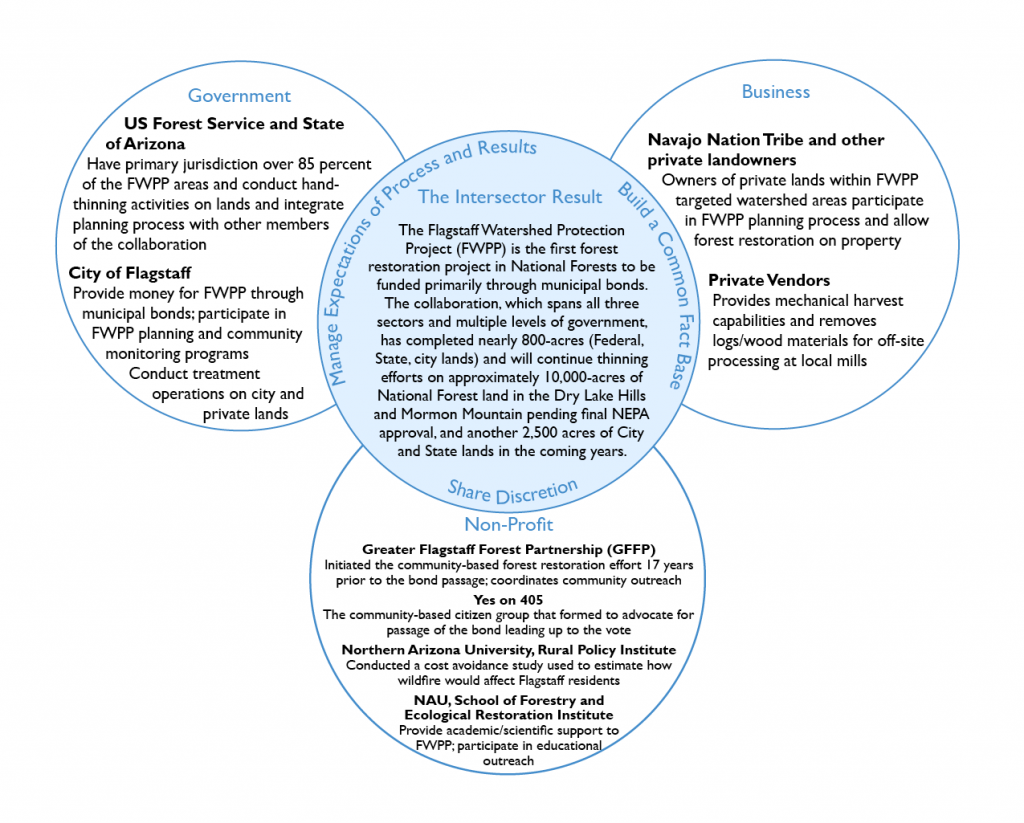
Paul is the Flagstaff Fire Department’s Wildland Fire Management Officer, past-President of GFFP, and Project Manager of FWPP activities for the city of Flagstaff. He graduated from the School of Forestry at Northern Arizona University (NAU) in 1977. After graduating, Paul spent the first 20 years of his career working in forestry and fire management in Colorado before returning to Flagstaff in 1997. He attributes the accomplishments of FWPP to the numerous individuals and agencies that actively engaged in the effort to make FWPP more than just a dream.

Intellectual Thread
Paul is the Flagstaff Fire Department’s Wildland Fire Management Officer, past-President of GFFP, and Project Manager of FWPP activities for the city of Flagstaff. He graduated from the School of Forestry at Northern Arizona University (NAU) in 1977. After graduating, Paul spent the first 20 years of his career working in forestry and fire management in Colorado before returning to Flagstaff in 1997. He attributes the accomplishments of FWPP to the numerous individuals and agencies that actively engaged in the effort to make FWPP more than just a dream.

Balanced Motivations
After 20 years of forestry and fire management in Colorado, Paul saw a job opening for a new wildland fire program at the Flagstaff Fire Department in 1997. At the time, extreme drought conditions, combined with poor forest management practices, led to one of the worst fire seasons in Flagstaff history. Fearful of more catastrophic wildfires, Flagstaff residents demanded action, and with the new Ecological Restoration Institute at NAU, progressive USFS land managers, and eager environmental groups, Flagstaff had all the elements and political will needed to reevaluate forestry practices in the region. Recognizing this as an opportunity to make a real difference doing something that he loved in a region receptive to change, Paul left his position in Colorado to pursue collaborative, landscape-based solutions to fire management in Flagstaff.

Contextual Intelligence
Paul has served on several inter-agency Regional and National Incident Management Teams, including time spent as the Incident Commander of the Rocky Mountain Type I Incident Management Team; an interagency, interdisciplinary team that comes together during an all-hazard emergency response to provide management leadership across sectors. His understanding of how fire impacts the local community, including how to identify people or businesses at risk, how to manage finances and resources across multi-level projects, how to identify constraints to progress, how to identify key performance indicators, and how to build comprehensive management teams, has provided him with the insight that no single agency can handle a large fire on their own. The process needs to include stakeholders from different agencies, backgrounds, and experiences. Paul recognizes that while including these various perspectives might make the initial collaborative process slow and sometimes arduous, over time, it results in lasting benefits. For example, when Paul joined the Flagstaff Fire Department, his first forest treatment project took place on a small 1-acre land parcel, but lasted several months because of a thorough, community-based approach. At the time, no one in the community had ever experienced forest restoration, and in order to unite all three sectors, Paul believed everyone in the community needed to express their concerns. If Paul had tried to streamline the initial process to save money and time, he would have likely faced lasting community opposition to what now has become routine forest practice. In fact, Paul’s awareness of the relevancy of his past experiences and ability to apply that collaborative knowledge to FWPP has likely contributed to the speed at which FWPP has progressed.

Integrated Networks
Paul has a working relationship with many of the key partners involved in FWPP that dates back to the start of his career. For example, Paul’s relationship with Dr. Wally Covington, Director of the Ecological Restoration Institute at NAU, began in Paul’s final year at NAU when Dr. Covington first became a forestry instructor; and Paul’s first boss in Colorado in 1977, Jim Hubbard, now serves as Deputy Chief at USFS in Washington, DC. These established relationships with two integral members of FWPP, colleagues who recognize Paul’s credibility and experience, has allowed the collaboration to quickly build capacity as well as ensure trust amongst stakeholders.

Share a vision of success
A shared community vision of a safer Flagstaff developed long before residents voted to fund FWPP. In 1996, the Flagstaff Fire Department, NAU, Grand Canyon Trust, and USFS formed GFFP to assess and reduce the growing risk of catastrophic wildfires within the region. Together, they unanimously developed one of the nation’s first landscape-based approaches to restoration forestry. Rather than focus solely on ecological concerns, GFFP expanded their scope to also include economic and social considerations. In order to bring public support into alignment with the mission of the collaboration, GFFP addressed human-posed barriers to action, led extensive public outreach, conducted economic viability analyses, and encouraged public involvement on management issues. After experiencing the type of wildfire risk reduction envisioned by FWPP through GFFP, Flagstaff residents accepted the need for immediate action and understood the ecological, economic, and social benefits of restoring Flagstaff’s fire-sensitive watershed.

Build a common fact base
Even with public support, land managers still needed to determine the best way to proceed with FWPP. They began by identifying two areas where a stand-replacing wildfire posed the greatest risk to critical Flagstaff infrastructure: Dry Lake Hills and Mormon Mountain. They then explored how to prevent a catastrophic wildfire by analyzing the 2010 Schultz fire, which occurred one ridge over and under comparable conditions. If a similar wildfire occurred on the steep slopes surrounding Flagstaff, the subsequent flooding and erosion could render 50 percent of Flagstaff’s drinking water unusable and cost the Flagstaff community approximately $1 billion in damages. After land managers developed a clear understanding of the threats, costs, and preventative measures, they approached city officials to cultivate a joint recognition of the relevant data and discuss solutions to their primary obstacle, funding. This comprehensive assessment of the problem and cooperative approach, allowed potential stakeholders to develop and define the boundaries of FWPP in just three months, before placing the $10 million bond question on the ballot.

Share discretion
FWPP is the first watershed protection project funded primarily by municipal bonds for work on federal lands outside of city limits. This unique funding structure poses a unique challenge to the allocation of decision-making authority. For any land management activity occurring on National Forests, USFS has the jurisdictional legal responsibility to act as the sole decision-maker; a responsibility they cannot share with any other entity. Likewise, similar jurisdictional issues also surround state, tribal, and private lands within the scope of FWPP. Conversely, the city of Flagstaff, as providers of the municipal bond, can refuse to pay for any management decision they feel extends beyond the best interests of Flagstaff residents. To prevent conflict at the decision-making level, FWPP’s diverse group of multi-level “decision-makers” meet monthly to discuss planning, development, and implementation of FWPP. Allowing each sector to express their desired outcome for the project prevents surprises during implementation, promotes continuity of action, and ensures that all stakeholders reach consensus before any official decision is made. In the two years since Flagstaff residents approved the $10 million bond, no conflicts have arose from this unique integrated approach to parallel decision-making.

Establish transparency of viewpoints
The ability of FWPP managers to actively acknowledge conflicting view-points has greatly contributed to the project’s community support and cross-sector buy-in. For example, forest managers recognize habitat loss due to catastrophic wildfire as the greatest threat to endangered species viability in the Southwest. Some environmental groups, however, have raised concerns over tree thinning activities and its effect on habitat availability for Mexican spotted owls, an endangered species. Rather than ignore these groups, FWPP managers created meetings to hear and respond to these concerns. This transparency even extends to the USFS’s Environmental Impact Statement, which does not list a preferred alternative for FWPP-related federal action. As a result, the public remains engaged and this creates an open atmosphere for comment on how USFS should proceed. This open flow of information creates a better interdisciplinary understanding of forest restoration, fosters mutual respect amongst stakeholders, and encourages comprehensive restoration policies.

Manage expectations of process and results
From the start of FWPP, Flagstaff officials wanted to maintain continuous communication with the community, and contracted with GFFP to conduct a variety of public outreach projects. This has included 25 workshops over the past 18 months to communicate FWPP progress and answer voter questions, and also includes a robust community monitoring plan that will measure public awareness and approval of FWPP over the course of the project. This outreach has also enabled land managers to make small adjustments to FWPP plans as they become immediately aware of community concerns. For example, land managers eased fears about the presence of industrial machinery near residential homes, when they agreed to move a temporary logging road 500-feet from its proposed location.
FWPP is expected to take between eight to ten years to complete. Currently approaching the project’s second year since the municipal bond measure passed, the collaboration has already established a number of intergovernmental agreements and memorandums of understanding between FWPP participants, including the City of Flagstaff, USFS, the State of Arizona, GFFP, and NAU. These agreements address the working arrangements of the collaboration and establish a financial management plan for FWPP. A steep-slope equipment demo project was also recently completed, and a Boundary Line survey, with Coconino County doing the work, is nearing completion. The development of the draft Environmental Impact Statement (EIS), however, represents the collaboration’s biggest effort so far. The public comment period for this draft EIS recently closed, and currently the collaboration has shifted to evaluating and responding to each of the 530 comments received from 107 individual respondents. In the future for FWPP, the collaborators will:
- Continue their review of public comments from the draft EIS, and work to incorporate any changes into the Final EIS.
- Continue efforts to analyze and accelerate treatment options in new areas not previously considered prior to the $10 million municipal bond. Prepare for large-scale implementation following the expected issuance of the Final EIS in January 2015.
- Continue community monitoring and tracking of the municipal bond, which has already grown by 16 percent over the past 18-months from small source donations, State grants, and additional federal funding.
